Welding is a joining materials process, causing fusion with the base metal melting. In addition a filler material is added typically to the joint. It forms a pool of molten material that cools to form a joint that is usually stronger than the base material.
Some of the best known welding types include:
- Electric Welding or Stick Welding – SMAW (Shielded metal arc welding) – uses an electrode with flux around it for the weld puddle protecting.
- Oxyacetylene welding or Oxy-fuel welding, oxy welding – uses oxygen and fuel gases for welding.
- Metal, Inert Gas – MIG or GMAW (gas metal arc welding) – uses a wire feeding gun that also flows a shielding gas (argon-based or argon + CO2) to protect the material from atmospheric contamination.
- Tungsten, Inert gas (TIG) or GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) uses a tungsten electrode (non-consumable) for welding weld. Uses inert shielding gas – helium or argon.
- Submerged arc welding (SAW) – with a blanket of granular fusible flux for protection from atmospheric contamination.
- Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) – as MIG except it uses filled with flux tubular wires.
- Electric resistance welding (ERW) – uses heat generated by the electrical resistance of the material.
- Plasma cutting – is not welding, but sometimes included in welding combo units.
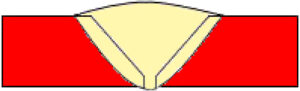
Butt weld used to connect nearly parallel but don’t overlap parts. It can be used for a continuous machine processing. Butt welding is usually accomplished with an MIG or arc welder.
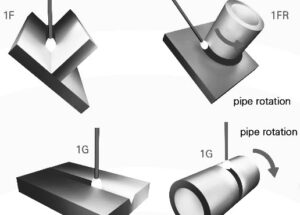
The flat welding position is the easiest position. The metal is flat, welding is going to move in a horizontal direction.
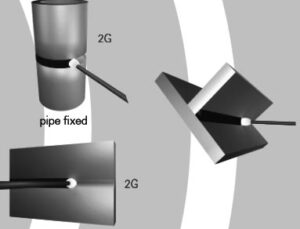
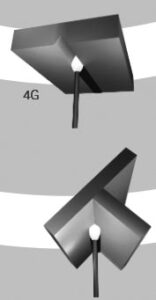
In the overhead welding position, the welding process is beneath the joint.
In the Vertical position the welds axis is almost vertical. When welding pipe in the vertical position the pipes axis is vertical and welding is in a horizontal position.
Here we’ll discuss welder machines types, welding process types were described here.
Most common welders are MIG, Arc, TIG, Gas, Spot
MIG welder has a handle with a trigger for a wire feed controlling. Handle feeds the wire to the weld joint from a spool. The wire runs through the liner. It has a protective gas feeding through the same cable. MIG welding is used most commonly in fabrication shops with where production is high, and there is no wind blowing away gas shielding.
Arc welder uses a welding power supply for an electric arc creating between the base material and an electrode to melt metal at the welding point. They can use either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) current.
Arc welders for home and DIY use are lightweight (15-20lbs or 7-9kg), features 120/230V auto reconnect operation and can work from a portable generator. With extension cord it can weld just about anywhere.
TIG welder
Tig welders electrode is made of tungsten (or alloy) and not consumed during welding. Tig welding torches are equipped with cooling systems (water or air). Manual TIG welding is a relatively difficult, due to the coordination required by the welder. TIG welding normally requires two hands, manually feeding a filler metal with one hand and manipulating the welding torch in the other.
Gas welder
Gas welding system consists of a fuel gas source and an oxygen source, two flexible hoses and two pressure regulators, a torch. similar to used for brazing and soldering.
A welding torch head can be identified by having only one or two pipes running to the nozzle, has no oxygen-blast trigger, and two valve knobs letting the operator adjust the fuel flow and oxygen.
Spot welder
In a spot welder work-pieces are held together with pressure exerted by electrodes. Spot welding system uses two copper alloy electrodes for concentrating welding current into a small “spot”. Large current through the spot melts the metal and forms the weld. The process does not cause excessive heating of the remainder of the sheet due to short time.
I’ll answer other questions. I have learned a lot from own experience and researching for this website.
So, send me a message, and I’ll list them below and it can be of use for everyone. I’ll list it without your email and full name.

